What is VAS? From SMS to «Smart Pipe»
Additional services for mobile operators, or VAS, are revenue-generating services that include all non-voice services provided by mobile operators.
Despite the fact that the term VAS comes from the telecommunication industry, today it is used in almost any field. Initially, VAS services were free or shareware services for a small fee, which mobile operators used to promote their main products.
In fact, telecommunication companies need VAS to increase the value of standard services, push subscribers to use them and increase the most important indicator for any operator — the average revenue per user (ARPU). Historically, such services as SMS, MMS, GPRS were considered mobile VAS. What do we see now? They are included in the standard offers. Hence, when we are talking about additional services today, we already mean something else.
What has changed in the VAS market?
The existence of VAS services has become possible due to the gradual development of cellular communication standards. Initially, mobile communication devices were unable to even send and receive text messages — by the way, they were the most popular and demanded additional service by mobile operators until the last couple of years.
Back in 1982, Conference of European Post and Telecommunications (CEPT) created a special group for mobile communications development — Groupe Special Mobile — in the French manner, since the French and Germans took the most active participation in that event. It was the beginning of the modern GSM communication standard (however, later a slightly different interpretation of the abbreviation appeared-Global System for Mobile Communications).
GSM became one of the first digital standards, indicating the transition to second-generation systems. Commercial system operation of the new communication standard began ten years later, in 1992. The advantages of GSM, as well as other second-generation cellular networks, are more reliable operation compared to analog standards, and the emergence of voice transmission services (such as call forwarding, call waiting, roaming services and other features that appeared in connection with the deployment of the second phase of GSM by 1997).
In addition to GSM, other digital cellular communication standards have existed and are widely used around the world, such as CDMA, which was once popular in Asia and North America. It was the transition to the second phase of the development of GSM networks that made it possible for mobile operators to offer their subscribers most of the additional services that we can observe today. However, the most popular service — text messages-appeared even before the introduction of phase 2 of GSM networks.
The integration of technology made it possible to receive and send a Short Message Service (up to 160 characters) long before the appearance of other services. One of the most significant consequences of the second phase of standard GMS was the invention of GPRS.
(General Packet Radio Service), which was more advanced than data transmission systems over switched channels CSD and HSCSD (High Speed Circuit Switched Data). This was the basis for the development of the mobile Internet. But we are coming back to text messages as the first and most popular of the VAS services. The first SMS with the symbolic content «Merry Christmas!» was sent in December 1992, on Christmas Eve, by Vodafone engineer Neil Papworth.
However, it took a while for the Short Message Service (SMS) to fight for its place in the market. Only in 1995, operators began to provide this service, and at first, it was free — due to a lack of confidence that the technology would be accepted by people. The SMS service, in addition to the practical results, has had serious social consequences. There was a whole new language for SMS. It was used to write dictionaries and novels, as well, a variety of emoticons which still exist today.
Soon after, the multimedia message services MMS were commercially launched, with the impetus for their emergence being the development of the mobile Internet at the turn of the century, which became possible just after the introduction of the GPRS packet data transmission technology. The Internet is one of the key technologies that has influenced the development of modern VAS services. Over time, the mobile Internet has become the most popular additional service provided by mobile phones.
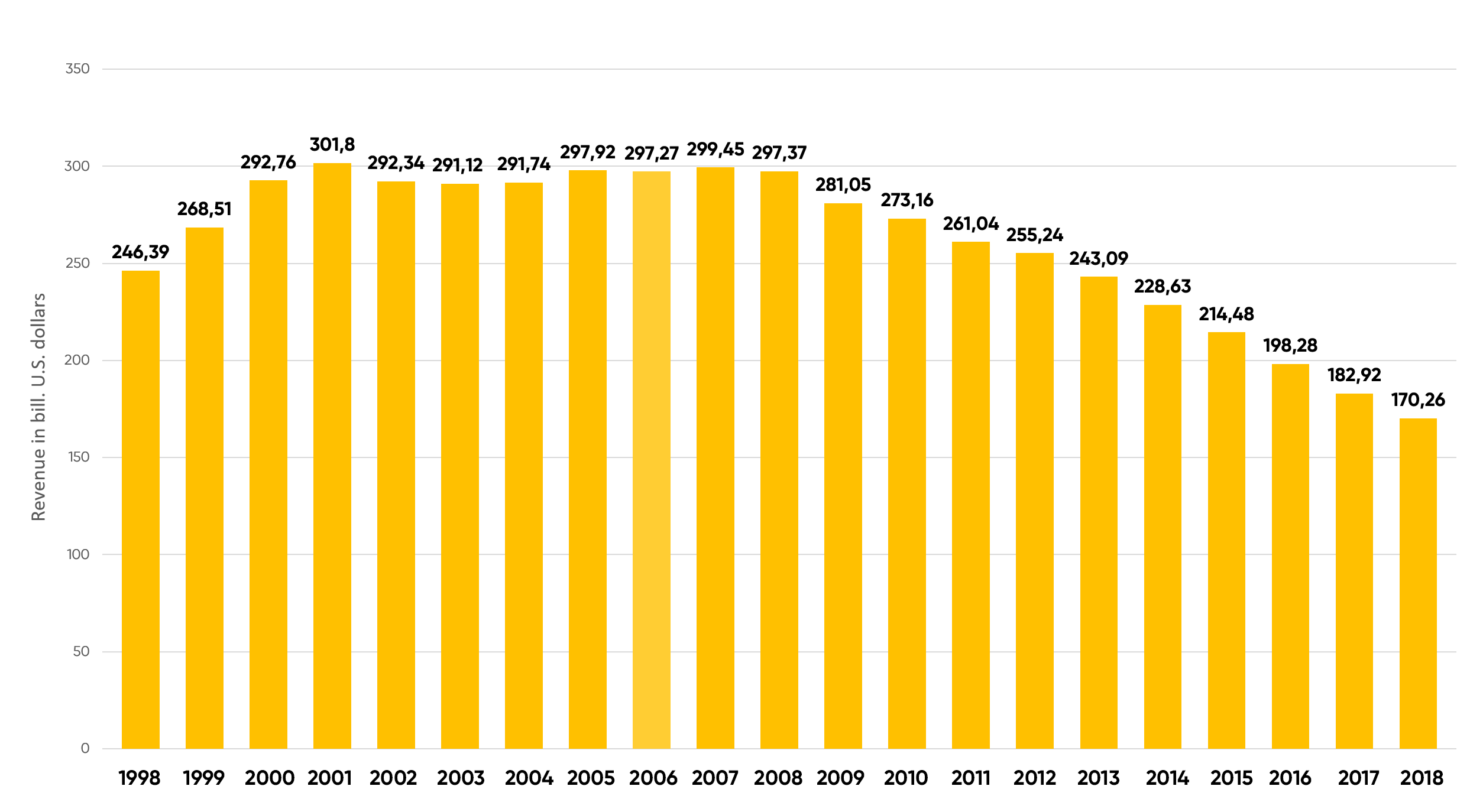
Back in the late 90s and early 2000s, services like phone calls and SMS showed an annual growth of more than 30%. After the crisis of 2007, growth first slowed down, and since 2013, it has stopped and even begun to show negative dynamics.
This statement is true both for the whole world and for individual local markets. For example, in the United States, revenue from telecommunication services showed growth only at the beginning of the first decade of the XXI century: the peak occurred in 2001. Following that, the market was relatively stable for seven years, but there has been a gradual decline since 2008, with the market «losing weight» by an average of $15 billion per year.
Technological development played an essential role. With the development of new generation 3, 4, and 5G networks based on high-speed data transmission, the number of additional services has increased, and mobile devices have gradually evolved into a work and entertainment tool.For mobile operators, entertainment services and mobile content became key factors of VAS services’ development at the beginning of the new millennium, and the market associated with these services began to be designated by the term mVAS.
For a long time, services for customizing mobile phones were extremely popular, allowing us to download melodies and pictures (or, as the most experienced cell phone users may recall, «text» melodies). Subsequently, such primitive customization has slowly begun to fade, since the growth of users’ mobile literacy, so people have found less expensive ways to personalize their mobile phones. This was also due to the increase in the capabilities of mobile phones and the emergence of new technologies for delivering, storing and playing mobile content.
All this has led to a gradual stagnation of ringtones and image services. Nonetheless, the old ones have been replaced by newer, more sophisticated methods of mobile phone personalization, such as Ring-Back-Tone services, which replace standard beeps with ringtones when calling a user.
It is obvious that mobile services are still earning most of the money for operators, but revenues are not growing, and companies have to explore new directions. Operators have no choice but to keep trying to meet the growing expectations of users. Therefore, they are moving in unusual directions for the telecommunication industry: from mobile television and music services to the Internet of things.
What about today?
Now, telecommunication companies sell mVAS as an additional function to their main services. At the same time, Mobile Value Added Services may well work independently. As a rule, they are essential not only to diversifying the main package of products. They provide additional opportunities for end users, while providing useful data to service providers.
Characteristics of Value Added Services:
- Increase the value of basic services.
- Are not basic services.
- Unique in terms of profitability.
- It can become a growth catalyst for the demand for standard services.
- They can work independently.
- Sometimes they are an addition to the main service.
VAS provided free of charge and play an important role in establishing the business reputation of the company. And those additional services that are offered along with the main ones at a discount, allow us to significantly increase our income.
It is also important to mention that telecommunication companies face competition from over-the-top services such as Netflix, Apple TV and Amazon Prime Video, and on top of that, we have VoIP represented by Skype as well as companies and providers of other digital content, like Spotify. Therefore, the growth of mobile operators is reduced due to the market diversity and the commercialization of smartphones. VAS helps to resist such business challenges.
Smart Pipe
The telecommunication business has recently been significantly transformed and has changed so much that there is no trace left of traditional operators, in the understanding of the last millennium. Will the operator be able to become a service platform, or will it take a place in the value delivery chain to the customer, or will it finally turn into a «data transmission pipe»? Today, the operator’s choice of services has expanded and, along with the traditional services: voice, data transmission, services and solutions for Big Data, Mobile VAS has also taken an important role.
And the concept of «Smart Pipe» itself is a combination of four platforms: analytics platforms, security platforms, connectivity platforms and an entertainment platform. Users need conditions for comfortable travel, booking tickets, e-commerce, services for maintaining a healthy lifestyle, playing sports, for financial transactions as well as managing objects and devices within the Internet of Things, and much more. Hence, «Smart Pipe» is the capabilities of modern technologies built into a holistic ecosystem based on VAS services.
At the same time, the focus is on the Web, on multi-channel products, and not on individual applications that are expensive to create and maintain. The phone account is a wallet for implementing a wide range of payment operations that can be done quickly, conveniently and safely.
The concept of «Smart Pipe» includes not only the payment of content from the phone through the model of direct debiting of funds from the user’s account using the DCB (Direct Carrier Billing) mobile billing that already exists today, but also other services: DCB for Stores, DCB for Pay, etc. Thus, a wide range of VAS services today represents the most promising direction for the development of operators.







 Searching...
Searching...